The expression alludes to the principle of functional incompleteness. A bird, for instance, requires two wings for flight; one wing alone cannot provide the necessary lift and balance. This concept extends beyond the literal to represent situations where a partial solution is insufficient to achieve a desired outcome. Consider, for example, a partially completed project; lacking essential components, it cannot fulfill its intended purpose.
Understanding this principle highlights the importance of comprehensive planning and execution. In engineering, design, and problem-solving, a thorough assessment of requirements and resources is crucial. Incomplete solutions often lead to wasted effort, inefficiency, and ultimately, failure. Historically, this understanding has been vital in various fields, from aeronautical engineering to the development of complex systems, driving the focus on holistic approaches and robust designs.
This concept serves as a foundation for exploring the necessity of complete solutions across diverse areas, including project management, software development, strategic planning, and organizational effectiveness. The following sections will delve into specific examples and methodologies that ensure the avoidance of such incomplete approaches.
Images References
Source: www.mdpi.com
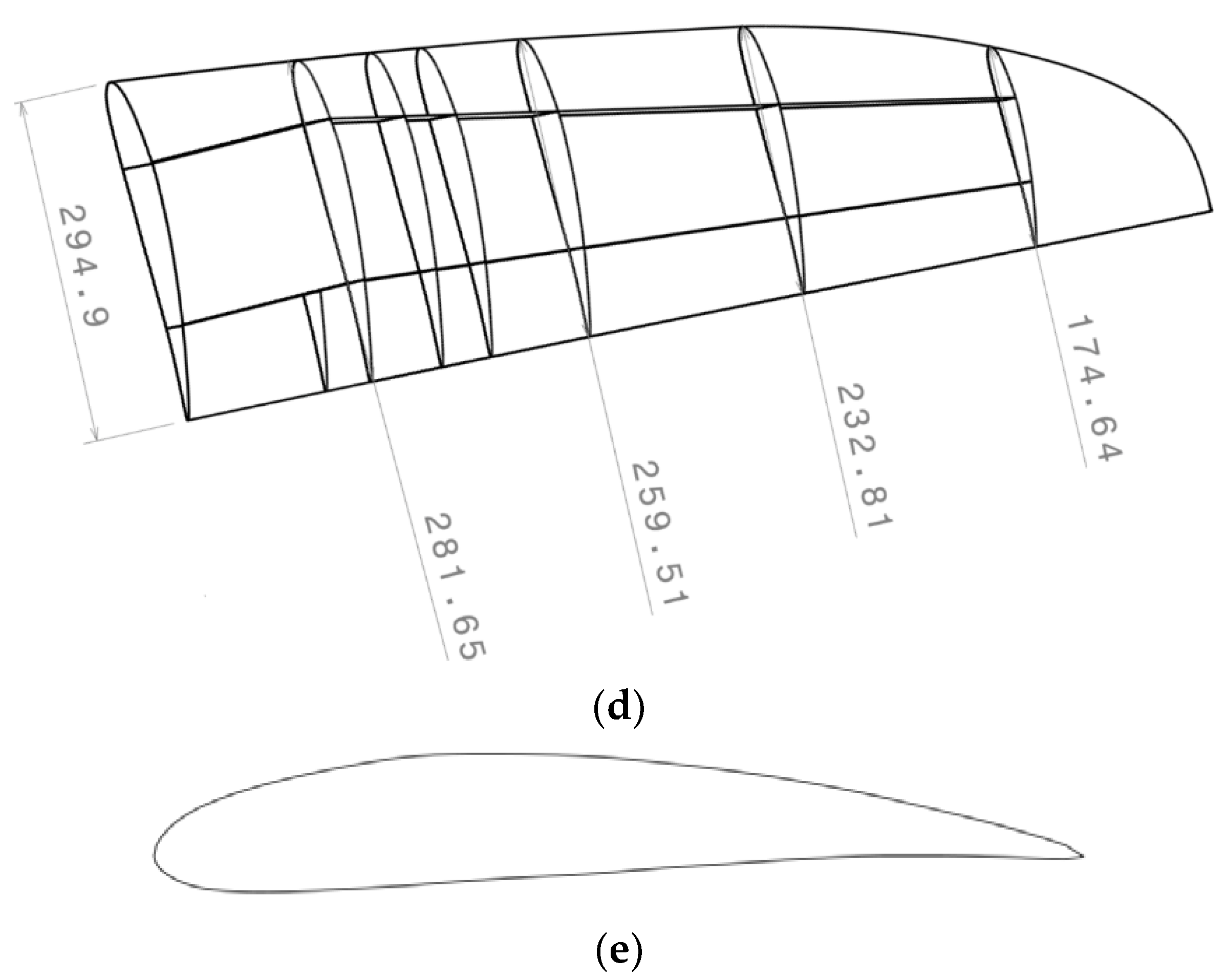
Aerospace Free FullText Shape Sensing for an UAV Composite Half

Source: gizmodo.com
How To Land a Plane That's Missing Half a Wing
Leave a Reply