Monoporeia are small, benthic amphipods, crustaceans inhabiting the sediment of marine environments, particularly in brackish and cold-water systems. They are often found in high densities, forming a significant component of the infaunal communitythe organisms living within the seabed. These organisms possess a segmented body, characteristically laterally compressed, with multiple pairs of legs used for locomotion and feeding. A crucial element of their biology is their burrowing behavior, influencing sediment structure and nutrient cycling.
Their abundance makes them a keystone species in many benthic ecosystems. They serve as a vital food source for commercially important fish and birds, impacting the food web’s overall health and productivity. Studies on Monoporeia populations provide valuable insights into the effects of pollution and climate change on marine ecosystems. Their sensitivity to environmental stressors makes them effective bioindicators, reflecting the overall health of the benthic habitat. Long-term monitoring of their populations contributes to effective conservation strategies and resource management.
Further exploration will examine the specific ecological roles of these organisms, delve into their life cycle and reproductive strategies, and discuss their significance in ongoing research concerning environmental monitoring and benthic ecosystem dynamics.
Images References
Source: www.sciencelearn.org.nz
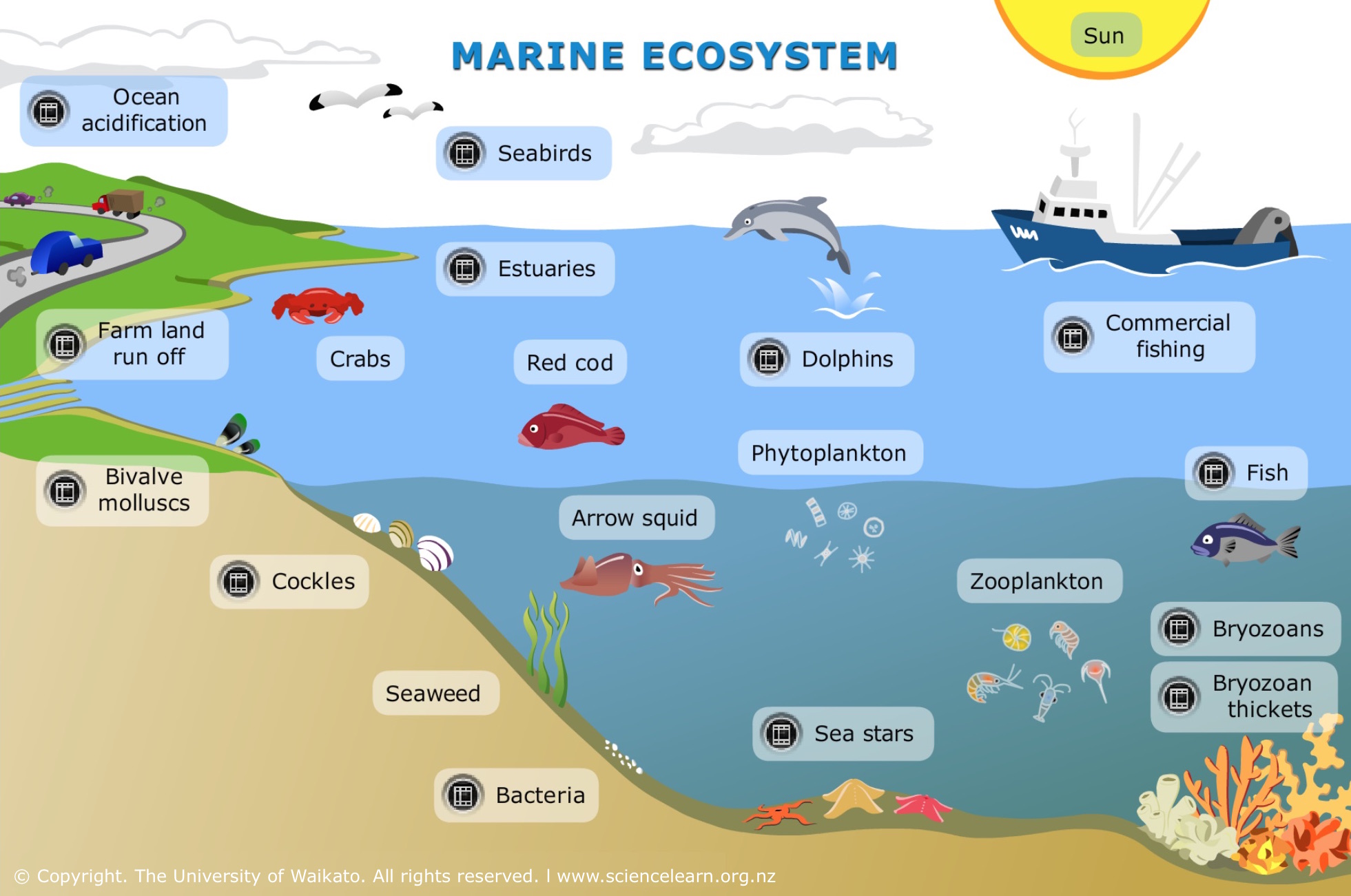
Marine ecosystem — Science Learning Hub

Source: www.youtube.com
Marine Biome YouTube
Leave a Reply