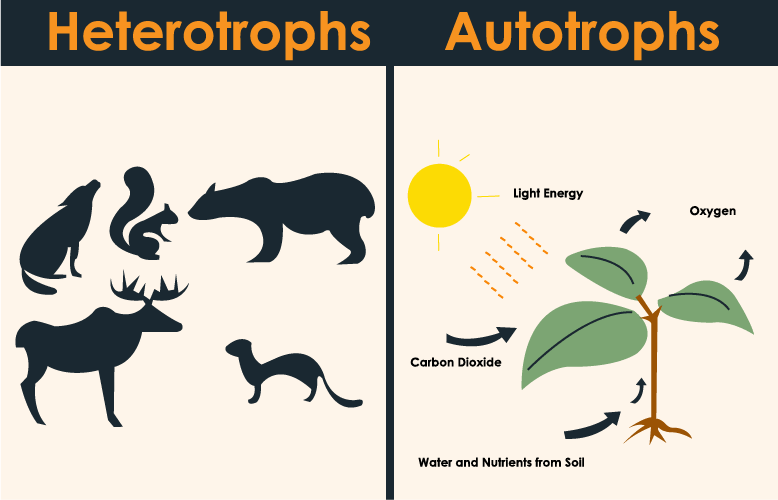
Organisms are classified based on their nutritional mode. Autotrophs, such as plants and algae, produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Heterotrophs, conversely, obtain energy by consuming other organisms. A jaguar, as a carnivorous mammal, falls squarely into the latter category, relying on the consumption of other animals for sustenance. Its diet consists primarily of large mammals like deer and capybaras.
Understanding an animal’s trophic levelits position in the food chainis fundamental to ecological studies. Knowing that a jaguar is a heterotroph helps researchers understand its role in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem balance within its habitat. This knowledge is crucial for conservation efforts, informing strategies for habitat preservation and population management. Furthermore, investigating the dietary habits of apex predators like jaguars provides insights into the health and stability of their prey populations.
This understanding of trophic classification facilitates further exploration of jaguar biology, including aspects such as its hunting strategies, energy expenditure, and overall ecological impact. Further research can delve into the jaguar’s specific prey selection, the effect of prey availability on jaguar populations, and the broader implications for the South and Central American ecosystems.
Images References

Source: sciencing.com
Heterotrophs & Autotrophs in the Tropical Rainforest Sciencing
Source: consumo372lessonlearning.z13.web.core.windows.net
Different Between Autotrophs And Heterotrophs
Leave a Reply