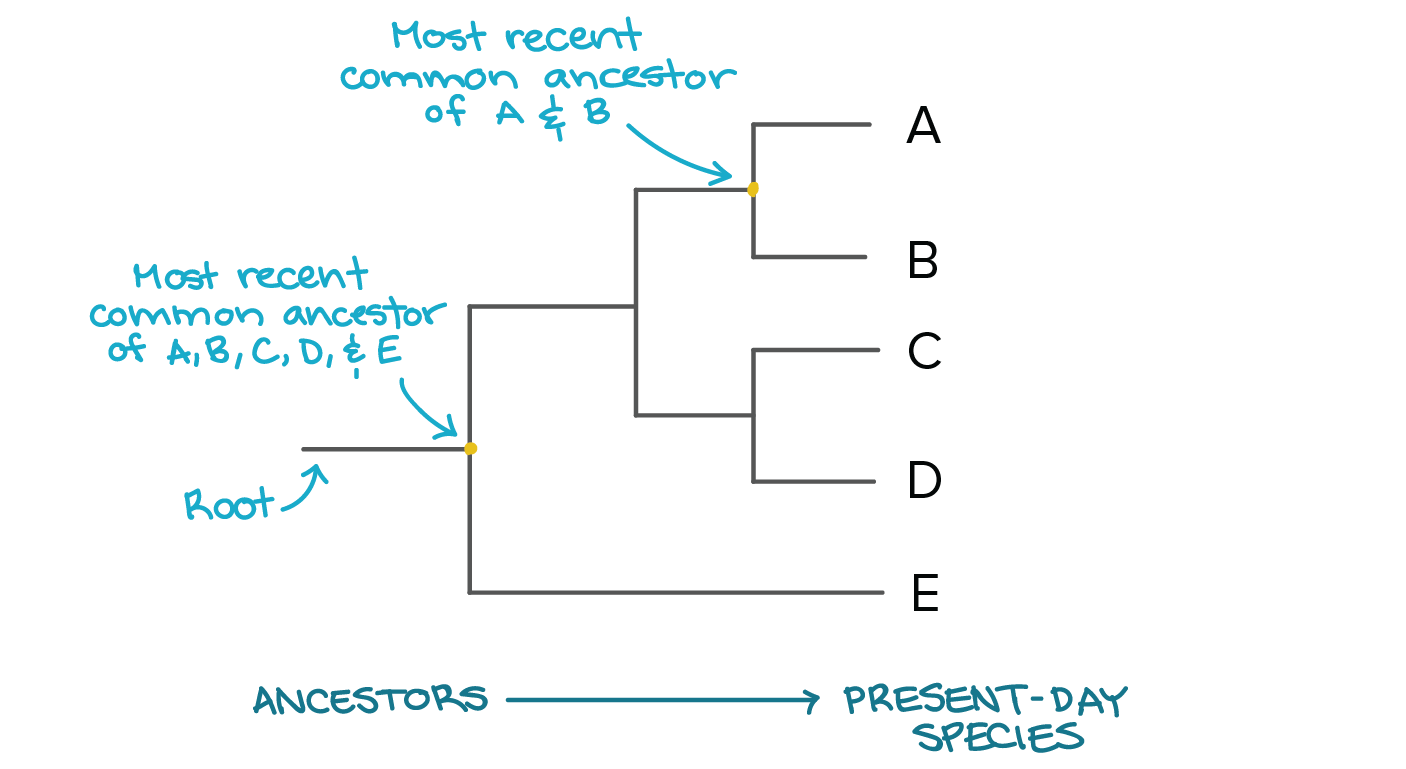
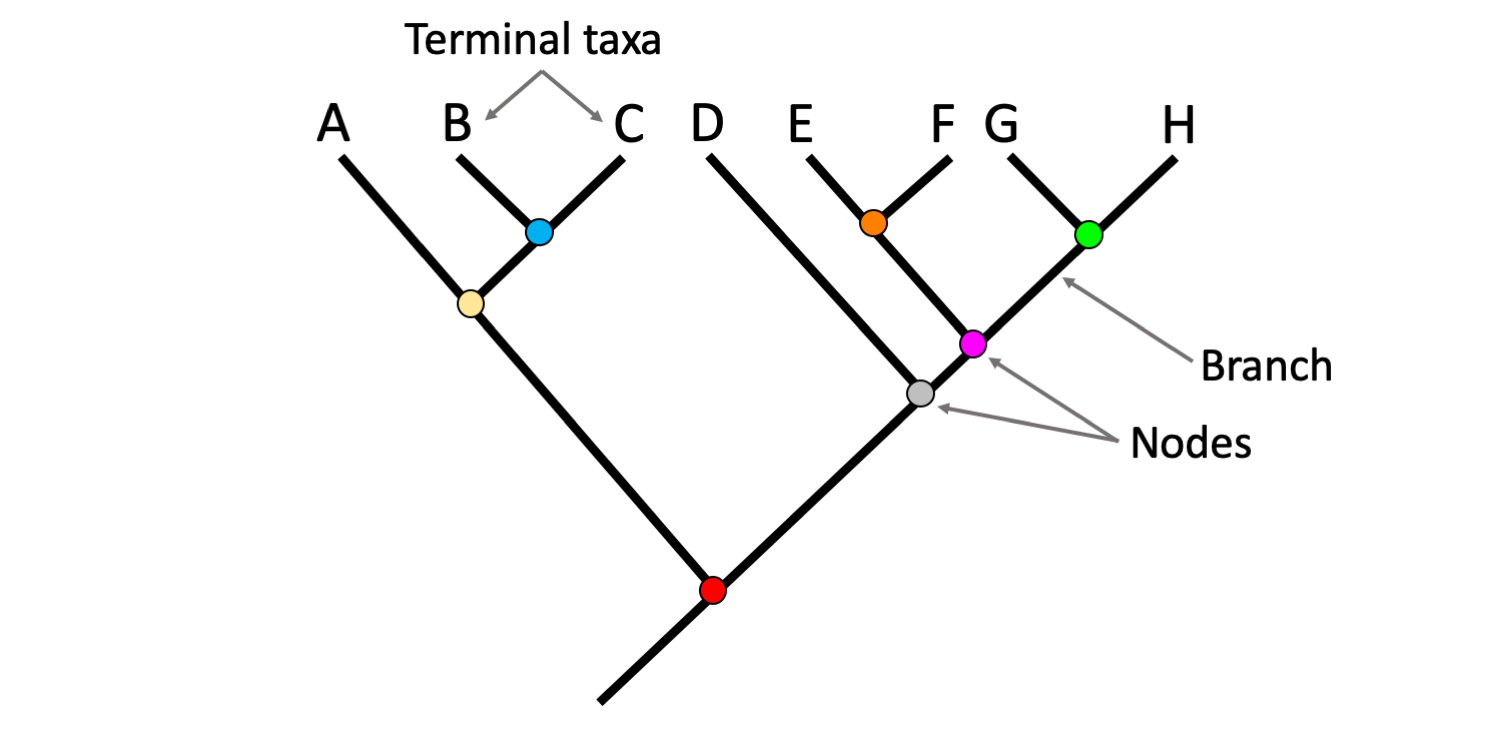
In a phylogenetic tree, a node represents the divergence of lineages. This signifies a point in evolutionary history where a common ancestor split, giving rise to two or more distinct descendant groups. For example, a node might show the divergence of chimpanzees and humans from a shared hominin ancestor. The characteristics of the descendants after this split can help determine the evolutionary relationships displayed.
Understanding these points of divergence is fundamental to reconstructing evolutionary history. They provide critical information for inferring evolutionary relationships, estimating divergence times, and tracing the spread of traits through lineages. Accurate representation of these points is essential for building robust and reliable phylogenetic analyses, enabling advancements in fields such as taxonomy, biogeography, and conservation biology. The study of these points has evolved considerably since the early days of phylogenetic analysis, with the development of sophisticated computational methods greatly improving accuracy and detail.
This understanding of evolutionary branching lays the groundwork for further exploration of specific lineages and their characteristics. Subsequent sections will delve into methods of phylogenetic tree construction, the interpretation of tree topologies, and the applications of phylogenetic analysis in diverse biological fields.
Images References
Source: alexandergroho.blogspot.com
Which Best Describes a Branch Point in a Tree AlexandergroHo
Source: alexandergroho.blogspot.com
Which Best Describes a Branch Point in a Tree AlexandergroHo
Leave a Reply