The phrase likely contains a misspelling. If “cooper” was intended to be “culprit,” “factor,” “cause,” or another word indicating a contributing element, then analysis would focus on the various aspects contributing to poverty. For example, lack of access to education, inadequate healthcare, systemic discrimination, and economic inequality are all significant factors perpetuating a cycle of poverty. These contribute to low earning potential, limited opportunities, and intergenerational disadvantage.
Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for developing effective strategies to alleviate poverty. Historically, approaches to poverty reduction have ranged from charitable giving to large-scale governmental initiatives focused on social safety nets, job creation, and economic development. These efforts aim to improve living standards, promote social mobility, and break the cycle of deprivation. The effectiveness of these approaches varies depending on context and implementation.
Further exploration of this topic will delve into specific contributing factors to poverty, examine historical and contemporary anti-poverty strategies, and discuss the ongoing challenges in poverty reduction. This will entail a detailed analysis of economic, social, and political factors impacting vulnerable populations globally.
Images References
Source: www.slideshare.net
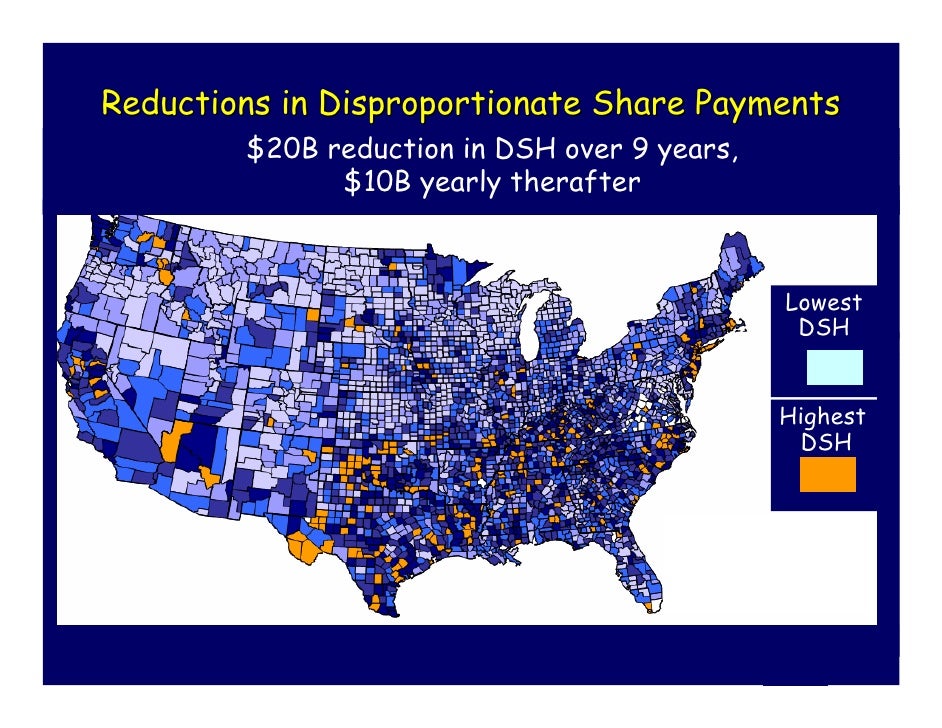
Cooper Health Care And The Affluence Poverty Nexus Detroit
Source: www.slideshare.net
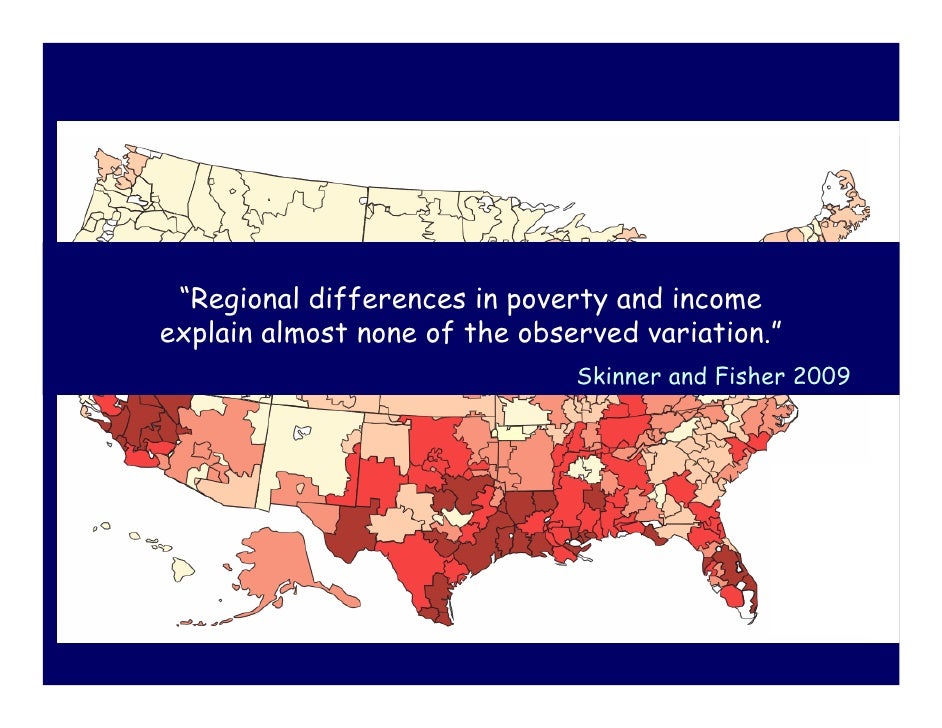
Cooper Health Care And The Affluence Poverty Nexus Detroit
Leave a Reply